Recently, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, CAS, has made remarkable achievements in nanopore technology research. The related findings have been published in renowned academic journals, including Chem. Eng. J., Talanta, and Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci.
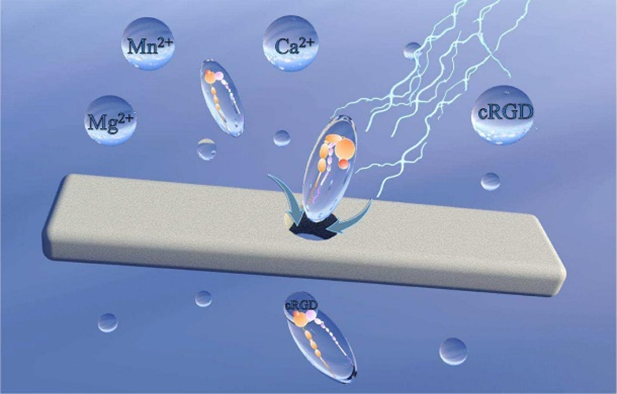
In integrin research, we have used nanopore sensors to characterize and modulate the conformation of integrin single molecules for the first time. It was found that there were two transport orientations for integrin αLβ2 and a single orientation for αVβ3 in the nanopores, and the transport transition threshold between the two appeared at 250 mV. At the same time, divalent metal ions can significantly modulate the integrin conformation, such as Ca2+-activated integrin αLβ2 with the largest geometric size. In addition, the oligopeptide cRGD and its derivatives specifically bind to αVβ3, which provides an important reference for understanding cell behavior and targeted therapy. (Characterization and modulation of the unimolecular conformation of integrins with nanopore sensors., Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 492, 152374.)
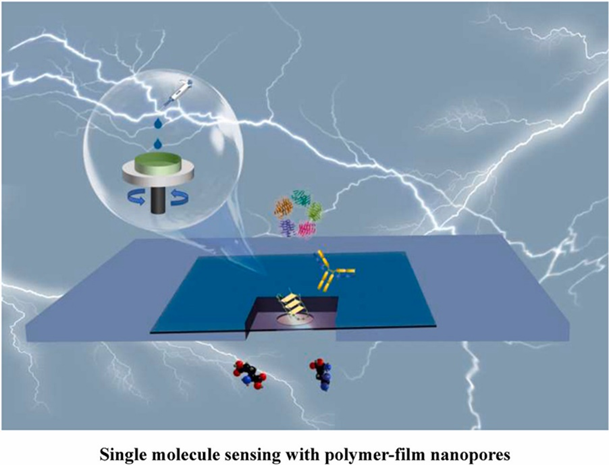
In terms of novel solid-state nanopores, we prepared a polymer (Azo-PMA) nanopores containing photo-switch azobenzene side chains. Nanopores of 2-20 nm can be fabricated on Azo-PMA membranes by controlled dielectric breakdown, which have good ion transport activity, pH tolerance and photo-response properties, and can work stably under high electrolyte concentration conditions, exhibiting low ionic current noise. The nanopores realize single-molecule resolution of nucleic acids and proteins, and can accurately detect the characteristic signals of individual nucleic acids and protein molecules, showing great potential in the field of biomolecule detection, which is expected to greatly improve the accuracy and efficiency of biomolecule detection, and provide more accurate analytical tools for biomedical research. (Azo-PMA nanopores of sub-20 nm length for unimolecular resolution of nucleic acids and proteins., Talanta, 2025, 285, 127402.)
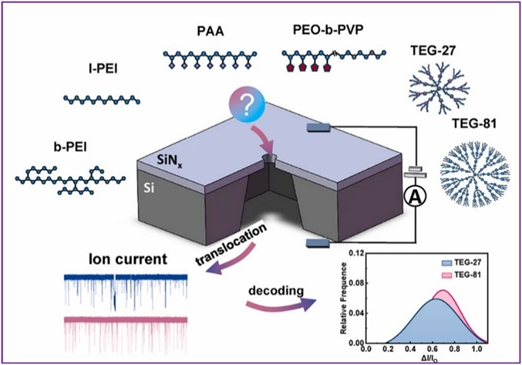
In the study of polymers and dendrimers, we studied the single-molecule conformation of polymers and dendrimers and their transport properties under different bias potentials and pH conditions with nanopores. It was found that the transport of PEI was significantly affected by pH, while the neutral block copolymer PEO-b-PVP showed a high capture rate under specific conditions. In addition, dendritic macromolecules exhibit a more elongated conformation under neutral conditions. These provide a theoretical basis for understanding the mechanism of macromolecule self-assembly and transfer. (Single - molecule resolution of the conformation of polymers and dendrimers with solid - state nanopores., Talanta, 2025, 286, 127544.)
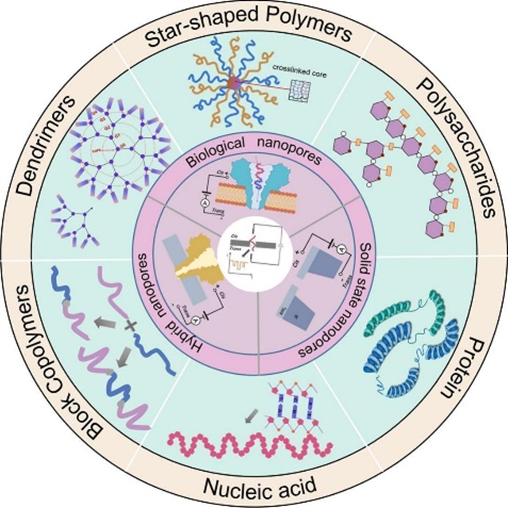
In addition, in the review paper, the classification, development, application and challenges of nanopore devices are introduced in detail, and their progress in analyzing the structure of various synthetic polymers and biomacromolecules is systematically summarized, so as to provide a clear framework and direction guidance for the research of nanopore technology in the field of conformation deciphering of macromolecules. (Single-Molecule Resolution of Polymers and Biopolymers with Nanopore Devices, Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2025, 338, 103417.)
Related paper links:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.152374;
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2024.127402;
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2025.127544;
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2025.103417.