At the microscale, addressing the challenge of quantitatively controlling the conditioning and dewatering process due to the variability of sludge properties, we investigated the synergistic effects of various physicochemical properties of sludge on the conditioning process. We established a multifactor coupled model for quantifying the optimal reagent demand and constructed a conceptual model of a 'dual system' to characterize the filtration and conditioning process of sludge. The correlation coefficient increased from 0.54 in traditional models to 0.93 in the new models. The research finding "Synergistic effect of organic matter-floc size-bound water and multifactorial quantitative model of optimal reagent demand in sewage sludge conditioning process prior to dewatering" was published in the journal "Water Research".
Figure 1 Sludge filtration and conditioning “dual-system” impact model
At the scale of rivers and reservoirs, change of hydrodynamic conditions induced sedimentation, water eutrophication and algal blooms in large rivers and reservoirs systems, thus a Hydrodynamic-Sediment-Water quality model for the whole Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) area was proposed, and the influence mechanism of the tide-type operation method on the hydrodynamic conditions, flux and retention rate of material in the TGR was revealed. The findings were published in the journal "Environmental Research", entitled Large-scale sediment and phosphorus transport in the Three Gorges Reservoir based on a new reservoir operation method.
Figure 2 Transport characteristics of sediment and phosphorus under the tide-type operation method based on a Hydrodynamic-Sediment-Water quality model
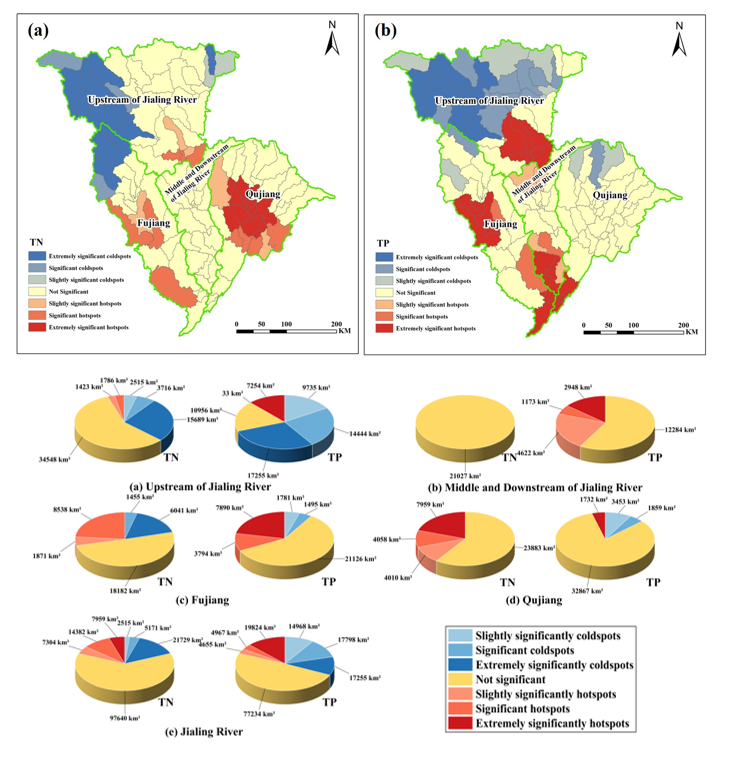
At the watershed scale, in response to the challenge of fragmented management approaches failing to achieve optimal governance outcomes in large and medium-sized watersheds, the Gi* statistic algorithm was introduced based on water environment modeling to reveal the aggregation characteristics of non-point source pollution within the watershed. This study offers a new perspective from the standpoint of watershed management for identifying critical governance areas for addressing water pollution issues in the Jialing River. The research findings, published under the title "Identifying critical regions for nitrogen and phosphorus loss management in a large-scale complex basin: The Jialing River" in the journal "Environmental Research," shed light on innovative approaches to identifying key areas for pollution control in the Jialing River basin.
Figure 3 Distribution and area characteristics of the key management areas of Jialing River based on the water environment model.
Articles information:
(1) Tan, X., Zeng, S.D., Chen, Z., Lv, M.Q., Tang, X.Y., He, X.X., Chen, Y.J., Wan, Y., Zhang, J.P., 2024. Synergistic effect of organic matter-floc size-bound water and multifactorial quantitative model of optimal reagent demand in sewage sludge conditioning process prior to dewatering. Water Research. 251, 121108. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2024.121108.
(2) Tang, X.Y., Zeng, S.D., Huang, G.X., Tong, S.C., Qiao, F., Ren, Y.X, Zhang, X.X., 2023. Large-scale sediment and phosphorus transport in the Three Gorges Reservoir based on a new reservoir operation method. Environmental Research. 233, 116386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116386.
(3) Ren, Y., Xia, J., Zeng, S., Song, J., Tang, X., Yang, L., Lv, P., Fan, D., 2023. Identifying critical regions for nitrogen and phosphorus loss management in a large-scale complex basin: The Jialing River. Environmental Research. 232, 116359. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116359.